What is methanol?
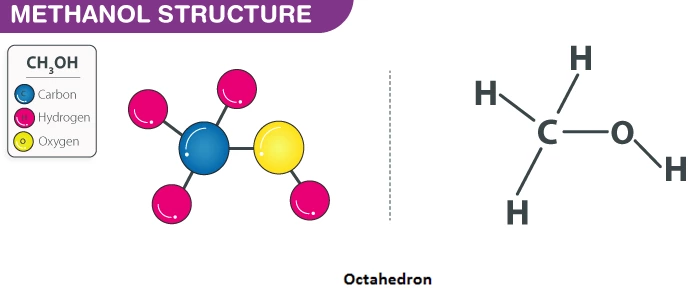
Methanol which is also known as methyl alcohol is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CH3OH. Since the hydroxyl group is chemically bonded to the carbon atom, it is not a hydrocarbon.
Methanol is made up of a methylu ground which is linked to a hydroxyl group. Some other terms are woof alcohol or methyl alcohol. The smell of methanol is rather of a distinctive kind that is sweeter and milder than ethanol. It is colorless and found to be volatile in nature. It is a poisonous liquid that is light and flammable too. If one were to consume methanol, it would be toxic for them and may also cause blindness. Acetic acid and formaldehyde are widely manufactured due to the use of methanol.
The first person to isolate methanol was Robert Boyle and he did it in the year 1661. It was created through the use of distillation of boxwood. Through the direct combination of carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst, methanol is produced in modern days. It is frequently used as a denaturant additive while manufacturing ethanol.
The molecular mass/ weight of methanol is 32.04 g/ mol. The density of methanol is 792 kg/ m^3.
Also, the boiling point of methanol is 64.7 degrees Celsius whereas the melting point of the same is -97.6 degrees Celsius.
Some of the uses of methanol:
- It is a chemical component which is used in polymers after they have been inverted to formaldehyde.
- Production of hydrocarbons is another use of methanol.
- In internal combustion engines, methanol is used as a fuel.
- It has been found to be excellent as an energy carrier.
- Methanol also acts as a fuel for boating stoves and while camping.
- During the synthesis of chemicals, methanol is used.
Why exactly is methanol important?
Methanol is a mandatory chemical that is used during chemical synthesis. It acts as a great substitute for gasoline and is thus used as a clean-burning fuel in automobile vehicles. It is also high octane. Synthetic ethyl alcohol is derived from the usage of wood drive methanol. These are the reasons why methanol is important and fruitful for us.
You must keep in mind that although methanol is a chemical compound with so many uses it is extremely poisonous and flammable in nature. If you directly ingest more than 10ML of methanol it could lead to blindness because of optic nerve damage or central nervous damage. One should not inhale methanol vapors either.
Some products that contain methanol are:
Antifreeze, paint thinners, and glass cleaners. Methanol is also present in fruit juices that have been distilled naturally but these are harmless methanol containing products.
Some facts about methanol:
It acts as a both a basic and as acidic. Due to the enzymatic breakdown of pectins, limited amounts of methanol is generated and found in wine. In the exhaled breath of the population, methanol is found too approximately 100 – 400 ppb which is below the limit of toxicity. At room temperature, methanol is a polar liquid. Coined by Dumas and Peligot in 1840, the term methyl was derived from the word methylene which was later on applied to be called methyl alcohol. In 2006, the large amount of methanol was discovered in space by astronauts at the jodrell bank observatory.
Catalysts like copper are used to efficiently produce modern methanol as it is capable of operating in lower temperatures. The most economical and widely used feedstock for methanol production is natural gas. In China, Coal acts as a popular feedstock for methanol production. Methanol was used as a fuel in several German military rocket designs during World War II. Back then, it was called M – stoff. Dimethyl is used as a chemical derivative for methanol which has substituted for chlorofluorocarbons and acetic acid. Keep in mind, that methanol is more difficult to ignite than gasoline.
A major drawback to methanol fuels is that is corrosive in nature to some metals, for example, aluminum. Although methanol is considered a weak acid, it has shown to attack the oxide coating which generally protects the aluminum from corrosion. Organic methanol (alcohol) is the result of the production of wood or different organic material that has been considered as a renewable alternative to petroleum based hydrocarbons. Remember, haloalkanes with the same number of carbon atoms have a lower boiling point than methanol. This is because alcohols are connected via intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Alcohol is a weaker acid in comparison to water because the polarity of the O – H bond in alcohol is low.
Through the catalytic hydrogenation of carbon monoxide due to high pressure and temperature and in the presence of ZnO – Cr2O3 catalyst, methanol is produced
